TAI #183: GPT-5.2 Arrives with a Breakthrough on GDPVal and long context
Also, Gemini Deep Research API, GLM-4.6V, Devstral 2 & more
What happened this week in AI by Louie
While the last few weeks have been defined by a relentless back-and-forth between Google, Anthropic, and open-weight contenders, OpenAI reasserted itself this week with the release of GPT-5.2. On many measures, this is a larger incremental breakthrough than the somewhat disappointing (and cost efficiency-focused) release of GPT-5. It is designed to tackle the most demanding professional workflows and is a direct response to Gemini 3’s strong showing.
The headline achievement is GPT-5.2’s performance on GDPval, a benchmark designed to measure real-world economic utility. On this test, GPT-5.2 Thinking achieved a win/tie rate of 70.9% against human experts, a massive leap from GPT-5’s 38.8%. The Pro variant pushed this to 74.1%. In the span of a single model generation, AI has effectively graduated from a “skilled intern” to a “senior manager” for many knowledge tasks. GPT4o was the best model, scoring only 12.4% little more than a year ago. The model also dislodges Claude Opus from the top ranking and moves past the key 50% win rate vs human experts.
What makes GDPval different from standard benchmarks like MMLU or GPQA? It measures how well a model does real work rather than how well it takes a test. The benchmark consists of over 1,000 complex, multi-step tasks across 44 distinct occupations (law, engineering, nursing, and more), designed by professionals with 14+ years of experience. A task might be “analyze these three financial reports and create a slide deck summarizing the risks,” taking a human 7 to 9 hours to complete. Grading is blind, with a human expert comparing the AI’s output directly against professional human work. GPT-5.2 matches or beats human quality on the majority of these tasks, doing so roughly 11x faster and at less than 1% of the cost. Of course — these are still adhoc tasks rather than a full job, and the strong results still require a human expert providing relevant context and integrating expertise into their prompt — but the value potential of AI used correctly for everyday work tasks is now unquestionable.
Beyond GDPval, the model shows benchmark leaps vs 5.1 across the board. One standout is its 90.5% on ARC-AGI-1 with the Pro variant, crossing a threshold many researchers thought was years away. On the much harder ARC-AGI-2, which isolates novel fluid reasoning and pattern recognition, it scored 54.2%, far outpacing Gemini 3 and Claude Opus. This suggests the model is improvising solutions to novel logical puzzles, not merely memorizing patterns.
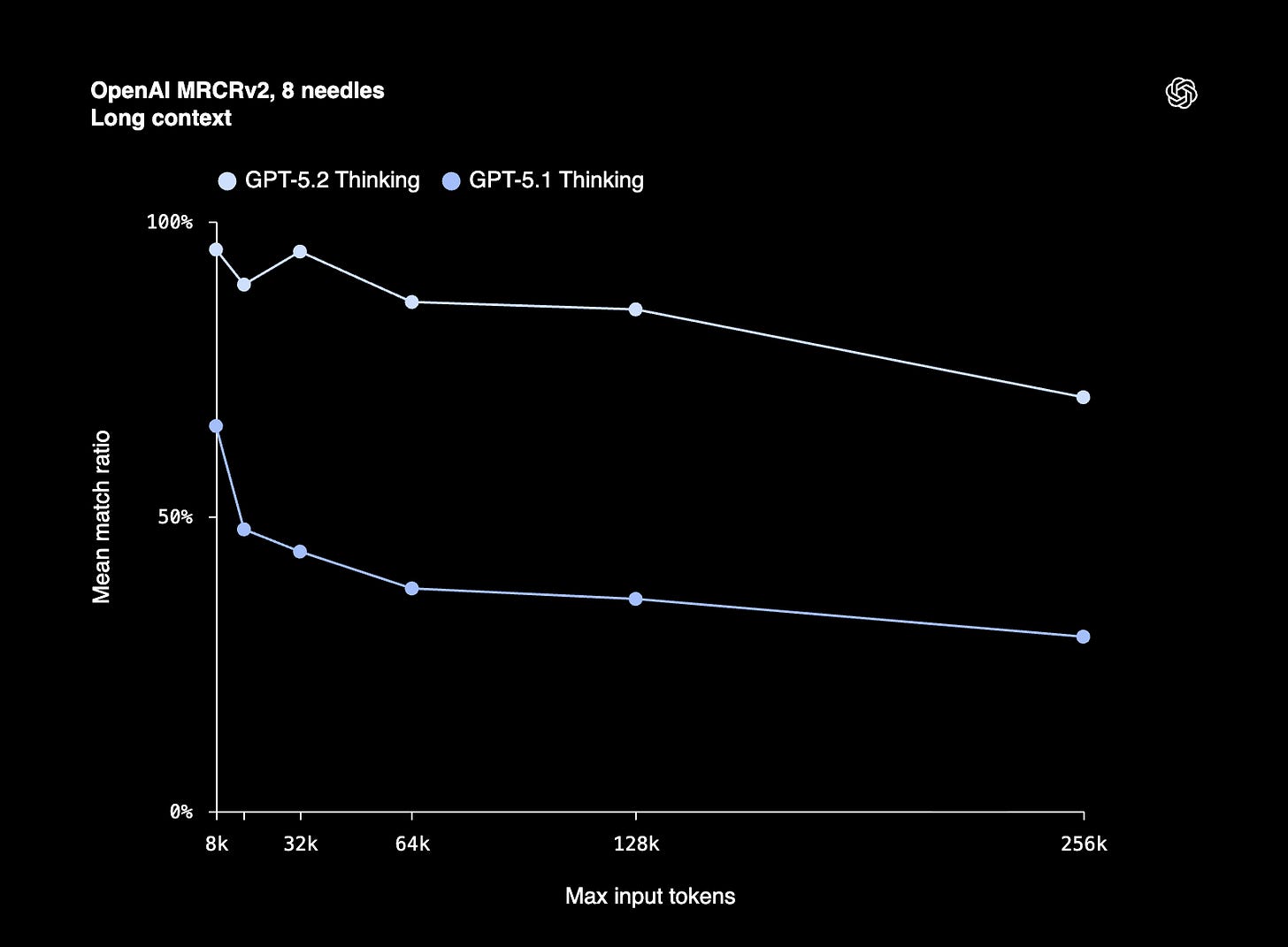
The most striking improvement in GPT-5.2, which likely aids many of these benchmarks, is long-context reasoning. On OpenAI’s MRCR (Multi-Round Co-reference Resolution) v2 benchmark, GPT-5.2 Thinking holds near 100% mean match ratio out to 256k tokens, while GPT-5.1 Thinking degrades sharply as context grows. This is the first time OpenAI has genuinely competed with Google on long-context performance. For context: GPT-5.1 Thinking dropped to just 29.6% accuracy at the 128k-256k token range on the 8-needle variant. GPT-5.2 Thinking scores 77% at that same range. On the 4-needle variant, GPT-5.2 achieves near-perfect accuracy out to 256k tokens, something no previous GPT model could manage. In practical terms, this enables professionals to work with long documents, contracts, research papers, transcripts, and multi-file codebases while maintaining coherence across hundreds of thousands of tokens.
GPT-5.2 also introduces a new xhigh reasoning effort level in the API, available on both Thinking and Pro variants. This is the most compute-intensive setting yet, allowing the model to work through problems for extended periods. GPT-5.2 Pro, in particular, can now work on complex tasks for over an hour in extended thinking mode, making it suitable for deep research, mathematical proofs, complex debugging, and multi-step enterprise workflows. For those of us doing serious knowledge work, this becomes our new go-to for tasks where accuracy matters more than speed. For writing, editing, and day-to-day coding, Opus remains our preferred choice due to its superior prose quality and personality.
The improvements come at a cost, both literal and figurative. GPT-5.2 is priced at $1.75 per million input tokens and $14 per million output tokens, roughly 40% higher than GPT-5.1 ($1.25/$10). GPT-5.2 Pro jumps significantly to $21 input and $168 output per million tokens. OpenAI argues that despite higher per-token costs, improved efficiency means the total cost to complete tasks may be lower. For output-heavy workloads (generation, long-form content), costs will increase noticeably. The model is also a step backwards in model personality. OpenAI optimized GPT-5.1 specifically for warmth and conversational personality after GPT-5 received criticism for feeling robotic. GPT-5.2 swings back toward enterprise task performance, optimized for factual accuracy, benchmark scores, and structured outputs as a response to Gemini 3’s competitive pressure. Early users describe it as more “rigid” in default tone. One tester noted that a simple question turned into 58 bullet points and numbered lists. GPT-5.1 remains more “chatty” and friendly, which many users prefer for lighter tasks.
This oscillation suggests OpenAI may need to branch model families rather than trying to optimize for both conversational warmth and enterprise performance in a single line. The tension between being a good chat companion and a good professional tool is proving difficult to resolve.
Why should you care?
The significance of GPT-5.2 lies in its reliability for “long-horizon” professional-level tasks. Previous models often fumbled when asked to coordinate complex workflows, like writing code, debugging it, then documenting it, without constant hand-holding.
The economic implications of the GDPval breakthrough are substantial. If a model can reliably perform 70% of senior-level tasks at less than 1% of the cost, the ROI for integrating these models into business workflows is no longer speculative. The barrier has shifted from model capability to organizational agility: can companies redesign their workflows fast enough to leverage these digital employees? GDPval itself still needs expansion to cover a far wider variety of real-world tasks and more complex multi-step iterative workflows, which will require significant investment to pay professional experts to create custom evaluation tasks. But OpenAI’s new focus on measuring real economic utility rather than academic test scores is likely to accelerate progress in ways that matter most: AI that can actually do the job, not just pass the exam.
— Louie Peters — Towards AI Co-founder and CEO
Hottest News
OpenAI has introduced GPT-5.2, its most advanced frontier model for professional work and long-running agents. GPT-5.2 is a family of three variants: Instant, Thinking, and Pro. It replaces GPT-5.1 Thinking as the main model for coding, knowledge work, and agents, while keeping the same 400k context and 128k max output. On key benchmarks, GPT-5.2 Thinking moves from 50.8 percent to 55.6 percent on SWE-Bench Pro, from 76.3 percent to 80.0 percent on SWE-bench Verified, and from 72.8 percent to 86.2 percent on ARC-AGI-1, and from 17.6 percent to 52.9 percent on ARC-AGI-2.
2. Google Launches Updated Gemini Deep Research Agent
Google released a re-imagined Deep Research powered by Gemini 3 Pro, confirming a shift from a report-writer to an autonomous research agent capable of long-form reasoning and complex analysis. Developers can now embed these capabilities via the new Interactions API, bringing step-wise planning, web use (where permitted), and multi-source synthesis into their own apps. Google says Deep Research will also surface in Search, NotebookLM, and Google Finance, with upgrades planned in the Gemini app.
3. Zhipu AI Releases GLM-4.6V: A 128K Context Vision Language Model
Zhipu AI has open-sourced the GLM-4.6V series. GLM-4.6V is a 106B parameter foundation model for cloud and high-performance cluster workloads. GLM-4.6V-Flash is a 9B parameter variant tuned for local deployment and low-latency use. Both models support native multimodal Function Calling so tools can consume and return images, video frames, and document pages directly. GLM-4.6V is trained for long-context multimodal understanding and interleaved generation, so it can read large mixed document sets and emit structured text with inline figures and tool-selected images in a single pass. The series achieves state-of-the-art performance on major multimodal benchmarks at similar parameter scales and is released as open-source weights under the MIT license on Hugging Face and ModelScope.
4. Mistral Open Sourced Devstral 2
Mistral has released Devstral 2, their coding model family, in two sizes: Devstral 2 (123B) and Devstral Small 2 (24B). Devstral 2 ships under a modified MIT license, while Devstral Small 2 uses Apache 2.0. Both are open-source and permissively licensed to accelerate distributed intelligence. They also introduced Mistral Vibe, a native CLI built for Devstral that enables end-to-end code automation. Devstral 2 achieves 72.2% on SWE-bench Verified and is up to 7x more cost-efficient than Claude Sonnet at real-world tasks. Devstral 2 (123B) and Devstral Small 2 (24B) are 5x and 28x smaller than DeepSeek V3.2, and 8x and 41x smaller than Kimi K2, making deployment practical on limited hardware.
5. Google DeepMind Released the FACTS Benchmark Suite
Google DeepMind introduced the FACTS Benchmark Suite, comprising three benchmarks to evaluate factuality in AI models: Parametric, Search, and Multimodal. The FACTS Parametric benchmark assesses models’ ability to accurately answer factual questions without the aid of external tools such as web search. All the questions in the benchmark are “trivia style” questions driven by user interest that can be answered via Wikipedia (a standard source for LLM pretraining). The resulting benchmark consists of a 1052-item public set and a 1052-item private set. Gemini 3 Pro leads in overall performance, with a FACTS Score of 68.8%.
Five 5-minute reads/videos to keep you learning
1. Enterprise RAG Without Compromise: Detailed Design
For organizations implementing enterprise RAG, this technical overview provides a blueprint for a production-grade system called Deepseek Copilot. It details the complete architecture, starting with a data ingestion pipeline and a hybrid retrieval method using vector and keyword searches to improve relevance. It also discusses strategies to mitigate hallucinations, the use of observability for monitoring, and a scalable microservices design on Kubernetes.
OpenAI’s state of enterprise AI report shows rapid workplace adoption of ChatGPT, with weekly enterprise messages up 8x and structured workflows up 19x year‑to‑date. Workers report 40–60 minutes saved per day, and 75% say AI improves speed or quality. Frontier workers send 6× more messages than median peers, as organizations shift from experimentation to deep, scaled integration.
3. How to Build Travel AI Agents Using Phidata and Qdrant
To address AI travel planners’ tendency to generate unreliable or fabricated recommendations, this article presents a multi-agent system that creates fact-based itineraries. It utilizes Phidata to orchestrate distinct agents for hotel searches and attraction discovery. These agents query a Qdrant vector database containing verified travel data, employing a hybrid search that combines dense and sparse vectors for accuracy. This RAG-based architecture ensures all suggestions are grounded in real-world information, effectively preventing model hallucinations.
4. Stop Shipping Blind Agents: Build On Your System of Record First
This article presents that for AI agents to be effective in enterprise software, they must be deeply integrated with core systems of record, such as CRMs and ERPs. This integration provides agents with a necessary digital spine, grounding them in reliable data, context, and secure operational tools. The author traces the evolution of SaaS toward a System of Agency, in which agents autonomously plan and execute tasks within workflows. This native approach, supported by vendors through new Agent Studios, is contrasted with less effective bolt-on bots, emphasizing that actual value lies in embedding AI directly into business processes.
5. The Omnibar Pattern: A Simple Architecture for Real-World AI
To reduce the friction of using AI, the author proposes the “Omnibar Pattern,” an architecture that shifts AI from a browser-based destination to an integrated, command-line utility. The approach centers on building a simple, centralized webhook using n8n to pipe requests from any client to an AI model. This piece details the four-node workflow for creating this universal AI pipe. It also explains how to develop specialized agents for different tasks, such as coding or summarization, and discusses evolving the system with features like automated routing and context-aware RAG.
Repositories & Tools
1. DeepCode is a development platform that automates code generation and implementation tasks.
2. CopilotKit is an agentic application platform that connects your app’s logic, state, UI, and context to agentic backends.
3. Sim is an open-source platform to build and deploy AI agent workflows.
4. Daytona is a secure and elastic infrastructure for running AI-generated code.
Top Papers of The Week
1. Long-horizon Reasoning Agent for Olympiad-Level Mathematical Problem Solving
This paper presents Intern-S1-MO, a long-horizon math agent that uses an LRM-based multi-agent system for reasoning, summarizing, and verification to solve IMO-level problems. The agent stores compact lemmas, performs multi-round hierarchical reasoning, and trains via the OREAL-H RL framework, achieving silver-level performance on IMO2025 and gold-level performance on CMO2025 while surpassing advanced LRMs on several benchmarks.
2. Weight-Sparse Transformers Have Interpretable Circuits
Circuit sparsity trains GPT-2-style decoder models with extreme weight sparsity enforced during optimization; most weights are zero, so each neuron has only a few connections. The research team defines circuits at the level of individual neurons, attention channels, and residual channels, and recovers circuits that often have tens of nodes and few edges across 20 binary Python next-token tasks. The work introduces encoder-decoder bridges that map between sparse and dense activations, allowing researchers to transfer sparse feature interventions into standard dense transformers and study how interpretable circuits relate to real production-scale models.
3. Native Parallel Reasoner: Reasoning in Parallelism via Self-Distilled Reinforcement Learning
This paper introduces Native Parallel Reasoner (NPR), a teacher-free framework that enables LLMs to self-evolve genuine parallel reasoning. NPR employs self-distilled progressive training, a Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization algorithm for adaptive task decomposition, and an NPR Engine for stable large-scale parallel RL. On eight benchmarks, NPR on Qwen3–4B gains up to 24.5% performance and 4.6x speedups with 100% parallel execution.
4. Wan-Move: Motion-controllable Video Generation via Latent Trajectory Guidance
Wan-Move introduces a scalable framework that brings precise motion control to video generative models. The method represents object motions with dense point trajectories, projects them into latent space, and propagates first-frame features along each trajectory, producing motion-aware latent conditions for off-the-shelf image-to-video models. Wan-Move generates 5-second, 480p videos and, on the new MoveBench benchmark, achieves motion controllability comparable to Kling 1.5 Pro.
Quick Links
1. Google releases LiteRT NeuroPilot Accelerator and MediaTek as a concrete step toward running real generative models on phones, laptops, and IoT hardware without shipping every request to a data center. LiteRT is the successor of TensorFlow Lite. It is a high-performance runtime that sits on-device, runs models in the .tflite FlatBuffer format, and can target CPU, GPU, and now NPU backends through a unified hardware acceleration layer.
2. Google released the Interactions API, which will enable you to connect Gemini models, Google’s built-in agents, and your custom agents using one API. The Interactions API introduces a native interface for managing complex context when building agentic applications that handle interleaved messages, thoughts, tool calls, and their states. It’s available for developers in public beta through the Gemini API in Google AI Studio.
Who’s Hiring in AI
Anthropic AI Security Fellow @Anthropic (Remote-friendly/UK/USA)
Product Manager @Mistral AI (Paris/London)
Senior Python Engineer — AI Agents @PandaDoc (Remote)
AI Bot Strategist @Coursera (Remote/Canada)
Applied AI Field Engineer @Instabase (Remote-friendly)
AI Engineer @Actalent (Remote/USA)
Interested in sharing a job opportunity here? Contact sponsors@towardsai.net.
Think a friend would enjoy this too? Share the newsletter and let them join the conversation.