TAI #182: The Reality of AI Agents in Production: Simple, Constrained, and Human-Verified
Also, Mistral & AWS Nova model releases, NeurIPS, Gemini Deep Think & more.
What happened this week in AI by Louie
While the industry holds its breath waiting for yet more imminent new model updates from OpenAI and DeepMind, this week offered a moment of reflection amidst the recent pace of new models. NeurIPS provided its annual feast of research papers, and we saw notable model releases from Mistral and AWS Nova. However, our attention was captured by a sobering, brilliant new study from UC Berkeley, IBM, and Stanford titled “Measuring Agents in Production.”
The paper, titled Measuring Agents in Production, contrasts the hype of fully autonomous agents with the gritty reality of what is actually working in the enterprise. Researchers surveyed 306 practitioners and conducted 20 in-depth case studies across 26 domains. The consensus? Production agents succeed through deliberate simplicity, not sophisticated autonomy.
The data reveals that engineers are trading autonomy for reliability. A striking 68% of production agents execute at most 10 steps before requiring human intervention, and 47% complete fewer than 5 steps. Furthermore, 70% of teams rely entirely on prompting off-the-shelf models without any fine-tuning. This challenges the narrative that successful agents require complex, custom-trained models. Instead, practitioners are prioritizing “bounded autonomy,” where agents operate within well-scoped action spaces rather than freely exploring environments.
One of the most interesting divergences found in the study is between survey respondents and deep-dive interviewees regarding frameworks. While 61% of general survey respondents use third-party frameworks like LangChain, 85% of the “hardcore” teams interviewed for case studies build custom implementations from scratch. The reasoning is pragmatic: core agent loops are often straightforward to implement with direct API calls, and advanced teams prefer minimal, purpose-built scaffolds over the dependency bloat and abstraction layers of larger frameworks.
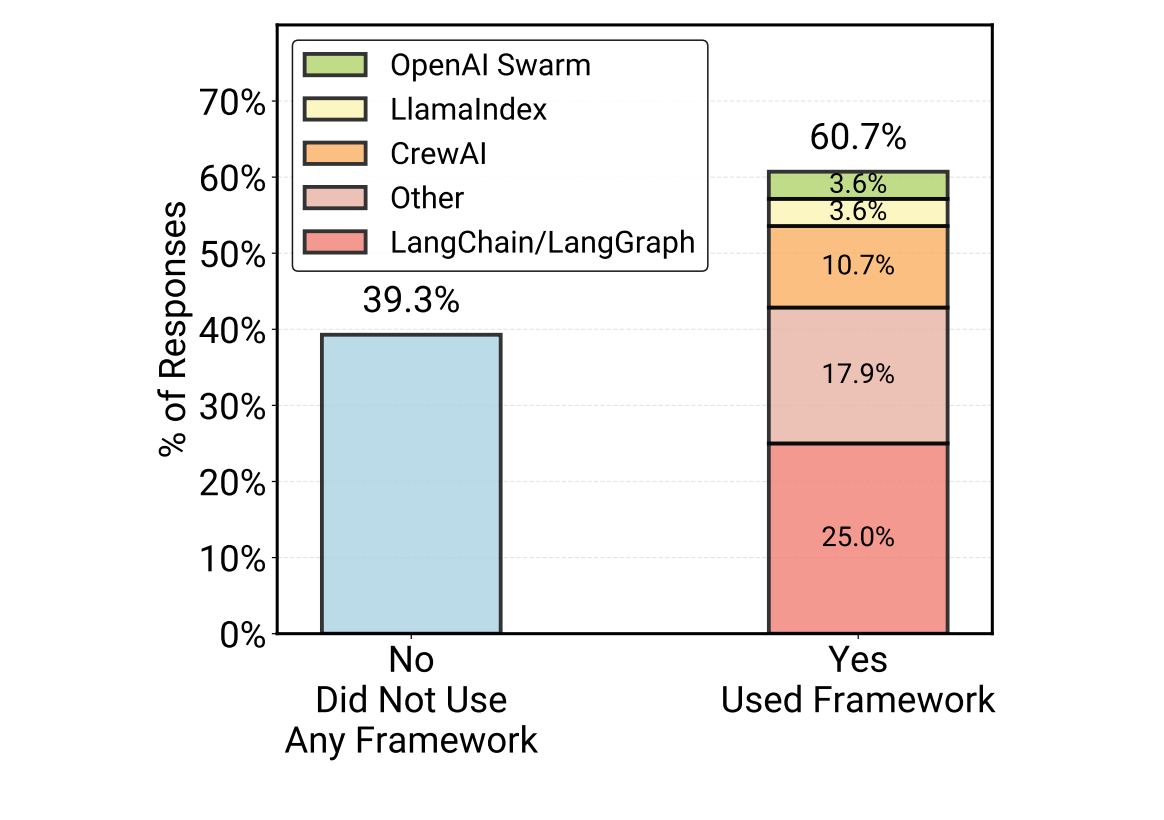
Model selection also followed a clear pattern. 17 of the 20 detailed case studies utilize closed-source frontier models such as Claude Sonnet 4, Claude Opus 4.1, and GPT-o3. Open-source adoption in production agents remains rare and is driven by specific constraints, such as high-volume workloads where inference costs are prohibitive or strict regulatory requirements regarding data privacy.
Finally, the study highlights that evaluation remains the primary bottleneck. Reliability is the top unsolved challenge, and public benchmarks rarely apply to domain-specific production tasks. Consequently, 75% of teams evaluate without formal benchmarks, relying instead on A/B testing and direct user feedback. Human-in-the-loop (HITL) evaluation dominates at 74%. Even when teams use “LLM-as-a-judge” systems (52%), they almost famously pair it with human verification to ensure safety and correctness.
This focus on building reliable, production-grade systems aligns perfectly with what we have been working on at Towards AI. We are soon releasing our “Agentic AI Engineering” in-depth course, where we will guide you through building and deploying two advanced, interconnected agents over the course of >35 in-depth lessons and notebooks.
Why should you care?
If you are struggling to build a fully autonomous agent that can navigate the world and solve any problem, you can stop beating yourself up. The data shows that very few companies have achieved this in production. The winning formula right now is finding a high-value workflow, constraining the agent’s actions to a predictable set of steps, and keeping a human in the loop for the final mile.
The revelation that elite teams are largely skipping agent frameworks in favor of custom code is also a significant signal for developers. It suggests that understanding the fundamental principles of agentic loops and API interactions is more valuable than mastering a specific library that might abstract away too much control.
Ultimately, the study confirms that the value of agents is not in novelty but in boring productivity gains. Organizations are happy to tolerate agents that take minutes to respond—66% of deployments allow response times of minutes or longer—because even a slow agent is vastly faster and cheaper than the human baseline. The industry is moving from the “wow” phase to the “work” phase, and simplicity is often the key to crossing that chasm.
— Louie Peters — Towards AI Co-founder and CEO
Hottest News
1. Google Launches Gemini 3 Deep Think Mode for Ultra Subscribers
Google has introduced Gemini 3 Deep Think mode within the Gemini app, adding heavier “thinking time” for complex math, science, and logic problems. Users can turn it on by selecting Deep Think in the prompt bar and choosing Gemini 3 Pro in the model menu. Google reports strong benchmark results, with 41.0% on Humanity’s Last Exam (no tools) and 45.1% on ARC-AGI-2 (with code execution), positioning the feature for harder multi-step reasoning rather than everyday queries.
2. Mistral AI Has Launched Mistral 3
Mistral AI has launched Mistral 3, a new generation of open multimodal and multilingual models that includes three compact “Ministral” systems and its most advanced release yet, Mistral Large 3. All models are available under the Apache 2.0 licence. The flagship Mistral Large 3 is a sparse mixture-of-experts model trained on 3,000 NVIDIA H200 GPUs, featuring 41 billion active parameters and 675 billion total parameters. While Mistral Large 3 targets high-throughput enterprise workloads, the company is also releasing Ministral 3, a new edge-optimised family in 3B, 8B, and 14B sizes. Each variant comes in base, instruct, and reasoning formats, all with multimodal capabilities.
3. Google Releases Titans Architecture
Google has unveiled “Titans,” a set of neural memory modules that learn what to retain and what to discard during inference, combining short-term attention with long-term memory to scale reasoning over millions of data points. The work, by Ali Behrouz, Peilin Zhong, and Vahab Mirrokni, introduces three variants: MAC, MAG (Memory as Gating), and MAL (Memory as a Layer) for different integration points. Titans is proposed as more effective than standard Transformers and modern linear RNNs on language modeling, commonsense reasoning, genomics, time-series, and “needle-in-a-haystack” tests. The approach trains and runs in a parallelizable fashion while maintaining stable recall across very large contexts.
4. AWS Unveils New Nova Models
Amazon has expanded its Nova lineup with Nova 2 Lite, Nova 2 Pro, Nova 2 Sonic, and Nova 2 Omni. Nova 2 Lite targets routine support and document workflows, while Nova 2 Pro is aimed at agentic coding, long-range planning, and multi-document analysis. Nova 2 Sonic is a real-time speech-to-speech model built for conversational AI with long-context interactions. Nova 2 Omni unifies text, image, video, and audio understanding and can generate both text and images, covering end-to-end multimodal use cases.
5. Google DeepMind Researchers Introduce Evo-Memory Benchmark and ReMem Framework
DeepMind has launched Evo-Memory, a streaming benchmark that turns static datasets into sequential task streams so agents must learn at test time and reuse strategies from earlier tasks. The companion ReMem framework extends ReAct with a Think → Act → Refine Memory loop, letting agents actively retrieve, prune, and reorganize memory during inference. Reported results show higher accuracy, higher success rates, and fewer steps on single-turn reasoning and long-horizon interactive tasks. The goal is to evaluate and improve agents that operate over evolving contexts, not just fixed chat histories. Benchmarks and code paths are geared to research and applied agent design.
6. OpenAI’s Confessions Method for Honesty
OpenAI has proposed Confessions, a training/evaluation technique where the model produces a second, honesty-only output that self-reports whether it followed instructions, cut corners, violated policies, or otherwise fell short. The confession is judged purely on the truthfulness of the behavior, separate from the quality of the main answer, to make missteps visible to users and systems. Early tests show substantially improved detection of undisclosed shortcuts and policy violations, increasing behavioral transparency without claiming to boost task accuracy by itself. The aim is to support safer deployments by flagging when to trust, review, or escalate a response. OpenAI frames this as early research with clear downstream uses in auditing and orchestration.
Five 5-minute reads/videos to keep you learning
1. Context Engineering Explained: The Anthropic Guide That’s Changing How Developers Work with AI
AI models can suffer from “context rot,” where performance declines as input information increases. This article expands on Anthropic’s guide to context engineering, a method for managing an AI’s context to overcome this limitation. It outlines three techniques: Compaction, which summarizes the conversation history; Structured Note-Taking, in which the AI uses external files for memory; and Multi-Agent Architectures, which delegate tasks to specialized sub-agents. It also covers the practical use of CLAUDE.md files for providing essential project information.
2. 4 Techniques to Optimize Your LLM Prompts for Cost, Latency, and Performance
To enhance LLM application performance, this analysis presents four practical techniques for prompt optimization. It recommends placing static content at the beginning of prompts to leverage token caching, thereby reducing costs and latency; positioning the user question at the end for improved response quality, particularly in long-context scenarios; using specialized prompt optimizers to refine prompt structure and eliminate redundancies; and creating custom benchmarks to systematically evaluate and select the best-performing LLM for a specific task.
3. The Ranking Revolution: Why Your RAG System Needs Learning to Rank (And How to Build It Right)
This article addresses a critical failure point in RAG systems: ineffective ranking of retrieved documents. It argues that providing irrelevant context to an LLM undermines performance, regardless of prompt engineering. It presents a two-stage retrieval architecture that involves a fast initial retrieval using bi-encoders or BM25, followed by a precise re-ranking of the top candidates with a cross-encoder. It also covers foundational concepts like the distinction between ranking and classification, listwise methods such as LambdaMART, and evaluation metrics such as NDCG.
4. Hierarchical Reasoning: What Happens When AI Stops Thinking Out Loud
Current AI reasoning methods, such as Chain-of-Thought, are often computationally expensive and slow. This article examines Hierarchical Reasoning Models (HRM), an alternative approach using a dual-network architecture inspired by human cognition. In this approach, a fast, low-level network processes immediate inputs while a slower, high-level network handles abstract reflection in a latent space, avoiding costly verbalized steps. The system learns both what to think through deep supervision and how long to think using a learned halting mechanism.
5. AI Cost Reduction Outlook: How to Cut Operational Expenses Smartly
This article details a four-layer framework for reducing operational costs with AI, moving beyond simple task automation. It explains how businesses can progress from direct savings (Surface Layer) to optimizing entire workflows (Process Layer), using predictive insights for proactive cost prevention (Intelligence Layer), and achieving compound improvements through network effects (Ecosystem Layer). It also outlines crucial technical considerations, such as scalable data architectures and MLOps, and provides a practical roadmap for implementation.
Repositories & Tools
1. Claude Quickstarts is a collection of projects designed to help developers quickly get started with building deployable applications using the Claude API.
2. AI Engineering Hub compiles in-depth tutorials on LLMs, RAGs, and real-world AI agent applications.
3. Open Code is an AI coding agent built for the terminal.
4. VibeVoice is a lightweight real‑time text-to-speech model supporting streaming text input and long-form speech generation.
5. cuTile is a programming model for writing parallel kernels for NVIDIA GPUs
Top Papers of The Week
1. DeepSeek-V3.2: Pushing the Frontier of Open Large Language Models
This paper introduces DeepSeek-V3.2, an LLM that unites high computational efficiency with strong reasoning and agent performance. The model employs DeepSeek Sparse Attention to cut long-context computation while maintaining quality. A scalable reinforcement learning framework and a large-scale agentic task synthesis pipeline drive GPT-5-level results and gold-medal performance in the 2025 IMO and IOI.
This paper introduces Qwen3-VL, a model that advances the Qwen vision-language series with dense and MoE variants that support interleaved text, image, and video contexts up to 256K tokens. The model strengthens pure-text understanding, long-context multimodal comprehension, and visual-math reasoning, while architectural upgrades, enhanced interleaved-MRoPE, DeepStack, and text-based time alignment, improve spatial-temporal modeling and temporal grounding for real-world multimodal applications.
The paper proposes Program of Thoughts (PoT), which uses language models (mainly Codex) to express the reasoning process as a program. Evaluating PoT on eight math and financial QA datasets in few-shot and zero-shot settings, they report roughly 12% average gains over Chain-of-Thought prompting and achieve state-of-the-art or near-state-of-the-art performance.
4. Gated Attention for Large Language Models: Non-linearity, Sparsity, and Attention-Sink-Free
This paper systematically compares over 30 variants of 15B MoE models and 1.7B dense models trained on a 3.5 trillion-token dataset. It finds that a simple head-specific sigmoid gate applied after the scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) consistently improves perplexity, benchmark scores, training stability, and tolerance to larger learning rates in both MoE and dense LLMs. This sparse gating mechanism mitigates ‘attention sink’ and enhances long-context extrapolation performance.
5. CLaRa: Bridging Retrieval and Generation with Continuous Latent Reasoning
This paper releases CLaRa, Continuous Latent Reasoning (CLaRa-7B-Base, CLaRa-7B-Instruct, and CLaRa-7B-E2E). This retrieval-augmented generation framework compresses documents into continuous memory tokens and then performs both retrieval and generation in that shared latent space. On multi-hop QA benchmarks like Natural Questions, HotpotQA, MuSiQue, and 2WikiMultihopQA, CLaRa’s SCP compressor, with 4x compression, outperforms strong text-based baselines such as LLMLingua 2 and PISCO.
Quick Links
1. Anthropic is launching Anthropic Interviewer to help understand people’s perspectives on AI. It aims to get a comprehensive picture of AI’s changing role in people’s lives and to center humans in the development of models. The Interviewer runs detailed interviews automatically at an unprecedented scale, feeding its results back to human researchers for analysis.
2. OpenAGI Foundation team has released Lux, a foundation model that operates real desktops and browsers and reports a score of 83.6 on the Online Mind2Web benchmark, which covers more than 300 real-world computer use tasks. It is available through the OpenAGI SDK and API console.
Who’s Hiring in AI
AI Researcher- MSc and PhD-Summer internship 2026- Research Lab @IBM (Israel)
System Software Engineer Intern, AI Infrastructure, Summer 2026 @NVIDIA (Shanghai, China)
Research Intern — AI Frameworks @Microsoft Corporation (Redmond, WA, USA)
AI Engineer @American Express (London, UK)
AI ML Engineer @Welocalize (Noida, India)
Junior Applied AI Engineer @Redhorse Corporation (Arlington, TX, USA)
Junior Data Scientist @WPROMOTE (Remote/USA)
Interested in sharing a job opportunity here? Contact sponsors@towardsai.net.
Think a friend would enjoy this too? Share the newsletter and let them join the conversation.




