TAI #168: Google's 'Nano Banana' and the Rapid But Incremental Pace of AI Capabilities
Also, Towards AI's new O'Reilly LLM fundamentals video course and our deep dive into LLM system design.
What happened this week in AI by Louie
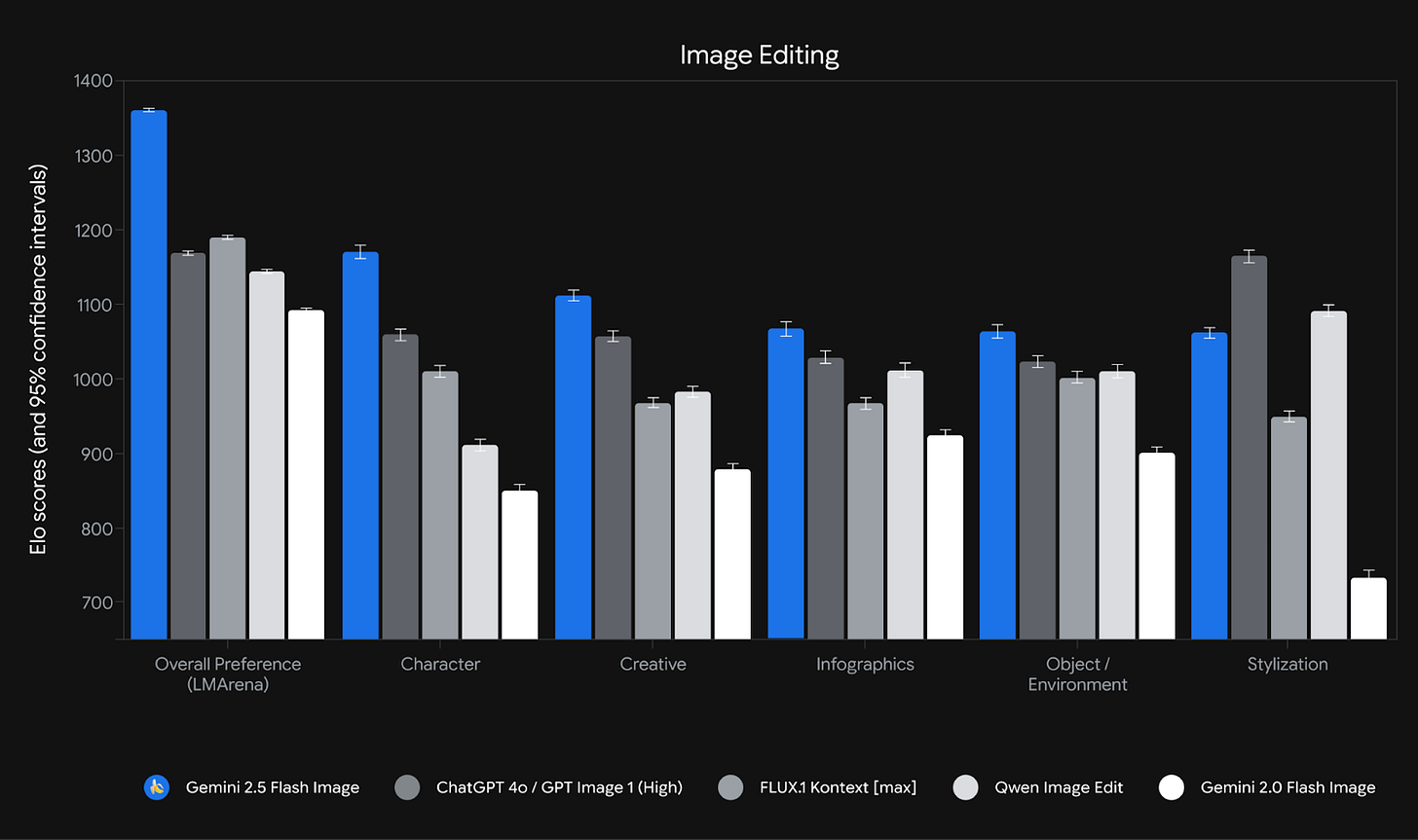
This week, Google DeepMind launched Gemini 2.5 Flash Image, a new model that feels like a significant maturation point for AI-driven visual creation. A few months ago, we discussed how native image generation within LLMs like GPT-4o was a breakthrough, moving us beyond the frustrating ‘potluck’ of traditional diffusion models. Gemini 2.5 Flash Image, tested on leaderboards under the codename “Nano Banana,” is the first model to truly polish that concept. It is now live in the Gemini app and available to developers, with the API endpoint currently in preview.
The performance is formidable. On launch, it topped the LMArena human-preference leaderboard for image editing with an Elo score of 1362, comfortably ahead of its rivals. This reflects its strengths in prompt adherence and visual quality. The model’s knowledge cutoff is January 2025. At a cost of roughly $0.039 per image via the API, it also makes high-volume, high-quality image creation economically feasible for a much wider range of applications. This compares to OpenAI’s gpt-image-1 API pricing, which costs approximately $0.01 (low), $0.04 (medium), and $0.17 (high) for square images.
The model excels at both image generation and editing, allowing users to blend multiple images (up to 3 inputs per prompt), maintain character consistency, and make targeted transformations using natural language. This is a huge step up from the typical process of starting each generation from scratch. New use cases include real-time creative workflows for storytelling, education (e.g., interactive tutors analyzing diagrams), augmented reality prototypes, and enterprise applications like product mockups, enabled by its speed (1–2 seconds per edit), low cost, and character consistency. The model’s level of iterative control is a game-changer for practical use cases. Some particularly fun experiments have seen attempts to get the model to render 3D images from 2D maps (including historical and fantastical locations) or 3D models from 2D architectural drawings. While not perfect, these results demonstrate a surprising grasp of physics and spatial awareness.
Why should you care?
This release continues to democratize access to high-quality visual design and marks the moment when native, conversational image AI moves from a promising novelty to a polished, enterprise-ready tool. For certain types of work, it becomes very hard to justify paying perhaps 100 times more for a fully human design that adds weeks of delay to an iteration process that can now take seconds. This doesn’t mean AI will replace human art; the need for art that creates a human connection and emotional response will always persist. However, it will undoubtedly produce countless new images we previously didn’t have the time, talent, or money to create, and it will absorb some design commissions.
One huge shift is in the workflow itself. The primary interface for visual creation is becoming a conversation. This moves the act of creation to a fluid, intuitive, and collaborative process with an AI partner. With 4o image generation, this conversation was still infuriating at times, but with Nano Banana, it is often becoming easy.
It is easy to forget that just two years ago, text-to-image was a low-quality novelty. When combined with other recent DeepMind releases, not only do we now receive high-quality images, we can even progress from text to image (with Nano Banana) to 8-second Video (with Veo 3) all the way on to creating interactive 3D worlds (with Genie 3).
We are seeing a similar capability leap in LLM text output with reasoning ability. A year ago, models like GPT-4o could only produce sloppy hallucinations on many complex tasks, whereas today, systems like GPT-5-Thinking can perform in-depth, multi-step research and analysis. Despite a huge amount of noise about AI progress plateauing, fundamental new capabilities like these continue to emerge each year.
That said, with the new reasoning model paradigm (where iterations happen more quickly via post-training) and so many strong AI competitors, the era of waiting years for a big, bundled step change upgrade like GPT-4 is likely over. We should now expect model improvements to be much more frequent, delivering these big leaps in similar time periods but via more incremental steps.
— Louie Peters — Towards AI Co-founder and CEO
Free for O’Reilly Members: 10-Hour LLM Fundamentals Bootcamp
If you’re an O’Reilly member, you can get free access to our 10-hour LLM Fundamentals course: a one-day, language-agnostic Bootcamp built for software professionals.
You’ll learn exactly when to Prompt, RAG, Fine-Tune, or Deploy Agents, and walk away with the practical knowledge needed to work with LLMs in real projects.
This five-part, bingeable video series covers:
Foundational AI knowledge and using LLMs
Building on top of LLMs
Evaluating RAG and LLM pipelines
AI workflows and agents with real case studies
Guardrails, advanced techniques, optimizations, and monitoring
🎯 Who it’s for: Software professionals ready to add LLM skills to their toolkit. 💡 What you get: A clear roadmap to move from basics to production-ready AI systems.
👉 Start learning now on O’Reilly
Also, this week with O’Reilly, we have published our latest work, 𝗟𝗟𝗠 𝗦𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗶𝗴𝗻 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹 𝗦𝗲𝗹𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 on Radar.
This (long-ish article) piece dives into the 𝗰𝗼𝗿𝗲 𝗱𝗲𝗰𝗶𝘀𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀 𝗲𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘆 𝗔𝗜 𝗲𝗻𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗲𝗲𝗿 𝗳𝗮𝗰𝗲𝘀: how to select the right model, balance performance with cost, and design production-grade LLM systems that actually scale.
We explored:
- The trade-offs between latency, cost, and accuracy
- When to use reasoning vs. fast models
- The pros and cons of open-weight and closed-API LLMs
- How to think about multimodality, context windows, and benchmarks
- A framework for system design that aligns with real-world constraints
Whether you’re evaluating models for a new product or optimizing pipelines in production, this article gives you the practical criteria and mental models you need to make the right choices.
Hottest News
1. OpenAI Releases an Advanced Speech-to-Speech Model and New Realtime API Capabilities
OpenAI has launched the GPT-Realtime model alongside updates to its Realtime API, enabling more advanced voice agents. The upgrades improve speech naturalness, reasoning, function calling, and intelligence. The API now also supports remote MCP servers, SIP phone calling, and image input, expanding real-time multimodal applications while maintaining cost efficiency.
2. Google Releases Gemini 2.5 Flash Image
Google has introduced Gemini 2.5 Flash Image, an upgraded image generation and editing model. It supports natural language transformations, character consistency, and multi-image fusion. Available through the Gemini API and Google AI Studio, it leverages native world knowledge to improve quality and realism in generated images.
3. Anthropic Unveiled Claude as a Chrome Extension
Anthropic is piloting a Claude extension for Chrome, initially available to 1,000 users on the Max plan. The extension enables users to interact directly with Claude within the browser. Safety evaluations highlight a reduced vulnerability to prompt injection attacks, addressing one of the primary risks associated with in-browser AI use.
4. Grok Introduced Grok Code Fast 1
xAI has launched grok-code-fast-1, a new model optimized for agentic coding within IDEs. The model is designed for stacks like TypeScript and Python, with pricing at $0.20 per million input tokens and $1.50 per million output tokens. It is available through launch partners, including GitHub Copilot and Cursor, targeting faster, more cost-effective coding assistance.
5. Alibaba Qwen Team Releases Mobile-Agent-v3 and GUI-Owl
Alibaba Qwen has released GUI-Owl, a multimodal agent model built on Qwen2.5-VL and extensively trained on GUI interaction data. Alongside it, Mobile-Agent-v3 leverages GUI-Owl as a foundational module, coordinating specialized agents, Manager, Worker, Reflector, and Notetaker, for complex, long-horizon tasks with dynamic planning, reflection, and memory.
6. Nous Research Team Releases Hermes 4
Nous Research has introduced Hermes 4, a family of open-weight models (14B, 70B, and 405B parameters) based on Llama 3.1 checkpoints. Built entirely through post-training methods, Hermes 4 features innovations such as DataForge and Atropos, with verification environments like Answer Format Training and Schema Adherence. The 405B model reaches 96.3% on MATH-500, 81.9% on AIME’24, 78.1% on AIME’25, 70.5% on GPQA Diamond, and 61.3% on LiveCodeBench, putting it in frontier-level performance territory.
Five 5-minute reads/videos to keep you learning
1. Crafting a Custom Voice Assistant with Perplexity
This guide shows how to build a custom voice assistant on a Raspberry Pi that delivers direct answers instead of search links. The system uses the Perplexity API to generate concise, single-sentence responses to complex and current questions. It integrates PicoVoice Porcupine for wake word detection, Google’s speech-to-text service for transcription, and gTTS for audio output, creating a lightweight, conversational assistant.
2. A Hands-on Agentic RAG Design Example
By adding agent-driven control to retrieval workflows, Agentic RAG enhances reliability in complex queries. The article demonstrates this through a basketball player information system, where the agent routes queries, validates results, and performs web searches when local data is insufficient. It also addresses practical deployment challenges such as parsing diverse file formats, mitigating cumulative errors, and maintaining module accuracy, providing a balanced look at real-world adoption.
3. Document Summarization & QA in RAG without Frameworks (PyMuPDF & ChromaDB)
This article details how to build a RAG pipeline from scratch using PyMuPDF and ChromaDB. Text and images are extracted from PDFs and split into chunks, with captions generated by a vision-language model. Each chunk is summarized, then combined into a final document summary. For Q&A, embeddings are stored in ChromaDB, allowing the system to perform semantic search and retrieve relevant context for accurate answers.
4. This Plug-and-Play AI Memory Works With Any Model
A method called Memory Decoder offers a universal way to adapt LLMs to specialized domains without retraining or relying on RAG. Acting as a small, pre-trained module, it can be attached to models like GPT, Claude, or Llama, enhancing them with domain expertise while preserving general knowledge. The approach improves efficiency across model families with minimal latency, providing a cost-effective solution for domain-specific applications.
Repositories & Tools
1. Fooocus is an image-generation software that works offline.
2. ActivePieces is an AI automation system designed to be extensible through a type-safe pieces framework.
3. HumanLayer enables AI agents to communicate with humans in tool-based and async workflows.
4. Koog is the official Kotlin framework for building and running robust, scalable, and production-ready AI agents across all platforms.
5. MiniCPM-V 4.5 is a series of efficient end-side multimodal LLMs.
Top Papers of The Week
This paper presents VibeVoice, a model capable of synthesizing long-form speech for up to 90 minutes with multiple speakers. It uses next-token diffusion to autoregressively generate latent vectors and introduces a continuous speech tokenizer that compresses data 80× more efficiently than Encodec, while maintaining fidelity and computational efficiency. VibeVoice authentically captures conversational dynamics and outperforms both open-source and proprietary dialogue models.
2. Performance Prediction for Large Systems via Text-to-Text Regression
This work proposes reframing regression as a text generation problem. The approach, called RLM, serializes industrial system state data into structured text, which serves as the input prompt. The LLM then outputs the target values as text strings, allowing performance prediction directly from raw text without complex feature engineering or rigid tabular formats.
3. Jet-Nemotron: Efficient Language Model with Post Neural Architecture Search
This paper introduces Jet-Nemotron, a family of models (2B and 4B parameters) that achieve up to 53.6× higher throughput than leading full-attention LLMs while matching or surpassing their accuracy. Its core innovation is PostNAS, a neural architecture search pipeline that retrofits pre-trained models for greater efficiency.
4. Self-Rewarding Vision-Language Model via Reasoning Decomposition
The paper presents Vision-SR1, a self-rewarding method that advances visual reasoning without external supervision. It decomposes reasoning into two stages: visual perception and language reasoning. The model first generates self-contained visual perceptions sufficient to answer a question, then reuses the same model to perform language reasoning on those perceptions to compute reward signals, improving accuracy through reinforcement learning.
5. Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
The StepFun AI team has released Step-Audio 2 Mini, an 8B parameter speech-to-speech large audio language model (LALM) designed for expressive, grounded, and real-time audio interaction. It integrates multimodal discrete token modeling, where text and audio tokens share a single stream. This enables seamless text–audio reasoning, real-time voice style switching, and consistent semantic, prosodic, and emotional outputs.
Who’s Hiring in AI
Software Engineer (Machine Learning) @Meta (Bellevue, WA, USA)
Software Engineer III, Machine Learning, Android AI Experiences @Google (Mountain View, CA, USA)
Mid-level Backend Software Engineer | Unverified Partner Content team @Wellhub (Brazil/Remote)
AI/ML Engineer @Cadmus (Jefferson City, MO, USA)
Senior Gen AI Engineer @Turing (India/Remote)
Python Software Engineer @econstruct (Cairo, Egypt)
AI Designer @Robert Half (Houston, TX, USA)
Interested in sharing a job opportunity here? Contact sponsors@towardsai.net.
Think a friend would enjoy this too? Share the newsletter and let them join the conversation.




Thank you for this insightful post on the incremental advancements in AI! The analogy of Google's 'Nano Banana' really highlights how small, consistent improvements can lead to significant changes. It got me thinking about how similar dynamics could apply across industries, including sports like basketball—where individual player growth is crucial for team success https://basketballstarsonline.io
Gemini 2.5 Flash Image feels like a true creative leap fast, consistent, and practical. It reminds me how creators pair visuals with trending sounds on a soundboard or meme soundboard. Whether you love a sound board or sound buttons free tools, comment on trending sounds and download them at https://soundboardw.com/