TAI #164: Generative AI Monetization Accelerates As ChatGPT Weekly Active Users Hit 13% of the Global Online Population
Also, OpenAI hits $12B ARR, Anthropic's $9bn 2025 forecast, Google releases Gemini 2.5 Deep Think, and more!
What happened this week in AI by Louie
Evidence of the LLM industry’s transition from research and hype to tangible revenue and adoption accumulated further this week. After years of GPU splurges and model-training moonshots, hard revenue from generative AI is finally starting to roll in, closing the gap between compute spend and cash flow.
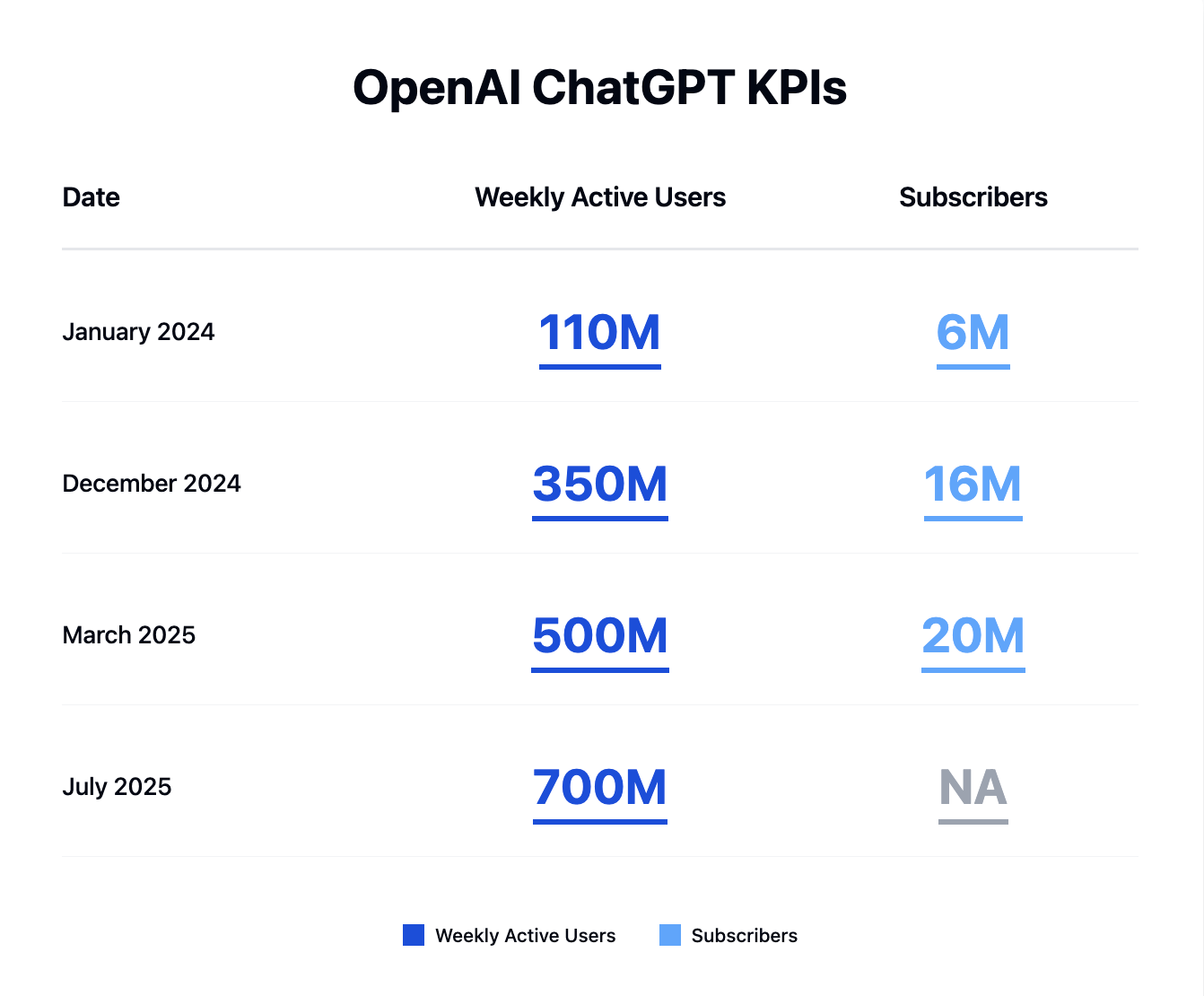
No company exemplifies this more than OpenAI, which is now generating $12 billion in annualized revenue, roughly doubling since the start of the year, with its expectations now to hit a $20 billion run rate by year-end. This growth is supported by over 700 million weekly ChatGPT users, which now accounts for a staggering 13% of the global population with internet access. This has doubled since December 2024 and is up 7x since January 2024. This user base spans both consumer and business customers, with OpenAI now counting five million paying business customers. To fuel this expansion, OpenAI has secured $8.3 billion in new commitments toward its massive $40bn funding round, valuing it at $260 billion. This success is also a key driver for Microsoft, whose AI business is now at an “over $15 billion annual run-rate.” Microsoft and OpenAI are also reported to be close to an agreement on the future of their partnership, with Microsoft expected to own 30–35% of a simplified OpenAI structure.
Meanwhile, OpenAI’s rival Anthropic is on an even faster revenue growth trajectory. Its annualized revenue has climbed 5x year-to-date to $5 billion, with projections to now hit $9 billion by year-end. A fresh funding round of up to $5 billion would push its valuation to about $170 billion, nearly tripling the $61.5 billion price tag it commanded in January.
While Anthropic’s growth is remarkable, its API-heavy revenue also presents a potential vulnerability; it’s easy for customers to switch if a better model emerges. However, user trust is a powerful moat, and Claude has become sticky in high-value workflows like coding within tools such as Cursor. This loyalty may soon be put to the test with the imminent release of GPT-5.
Google is also demonstrating rapid growth — its Gemini models processed 980 trillion tokens in June 2025 alone, a 100x increase from a little over a year ago, though it remains unclear how much of this is driven by AI search summaries versus direct API and Gemini app usage. The Gemini app itself now serves more than 450 million monthly active users, with daily requests up over 50 % versus Q1, and over 9 million developers have already built with Gemini models.
These revenue figures are finally starting to justify the monumental AI infrastructure investments. Collectively, Microsoft, Google, Amazon, and META have spent more than $600 billion on data centers and other capex in the past twelve months, with triple-digit capex growth over 2 years. For a long time, this capex growth dramatically outpaced cloud revenue growth, but that trend is now reversing as contracted business begins to materialize. All this activity has been reflected in the public markets, where Nvidia, the company supplying the foundational hardware for this revolution, has now become the most valuable company in the world.
This takeoff has been driven by a confluence of factors: breakthroughs in model capabilities through reinforcement learning and agentic systems, and the passing of a critical threshold for AI coding, first demonstrated by Claude 3.5 and accelerated by tools like Cursor. For example, Microsoft reported that its GitHub Copilot gained 5 million new users in the past three months, bringing the total to 20 million, while Anthropic plans to charge superusers of its AI coding software after some have consumed tens of thousands of dollars’ worth of compute per month.
Why should you care?
The soaring revenue figures at AI labs signal that the AI economy is no longer a future promise; it’s a present-day reality. This all suggests that both the long-speculated, world-changing benefits of AI and the significant risks of economic and labor force disruption are getting closer.
Yet, these same impressive figures also hint at how far we still have to go with AI adoption. The soaring revenues are largely driven by a small minority of paid power users concentrated in a handful of use cases, with AI for coding being the most prominent. Most people are still operating on free, consumer-grade plans that are unsuitable and often insecure for real work.
Even among those with paid subscriptions, most use only the default models like GPT-4o, when frontier models like o3, o3-pro, Gemini 2.5 Pro, Grok-4, Claude 4 Opus, or even open weight models like Kimi K2 deliver vastly superior results on many tasks. Broad experimentation with AI across the full spectrum of professional tasks remains nascent.
The upcoming release of GPT-5 may help reduce this problem, as we expect a more automated adaptation of AI compute usage and active parameters to the task at hand. However, with such a wide range of strong AI competitors and the inherent difficulty of robustly evaluating performance on your own specific workflows, the challenge of selecting the right tool and using it effectively will remain.
This creates a significant competency and productivity gap. The difference in output quality between a casual user and a power user who knows which model to deploy for which task is enormous. The companies that figure out how to bridge this gap — by investing in training and building sophisticated custom LLM workflows and agents — will gain a significant competitive advantage. For now, the advantage lies with those who learn to make that choice themselves.
The AI revolution is here, but its benefits will be unevenly distributed to those who actively learn to build or wield its most powerful tools. At Towards AI, our mission is to make AI accessible and to help as many people as possible join the group that benefits from this shift. If you want to help friends or family get on the right side of AI, please consider sharing our course platform. We offer a clear pathway for anyone, technical or not, to master using AI at work. For those looking to build with this technology, we also offer an advanced AI Engineer (or LLM Developer) certification. This program has starting points for everyone, from the coding novice to the experienced Python developer, and guides them all the way to building production-ready LLM tools and products.
— Louie Peters — Towards AI Co-founder and CEO
This issue is brought to you thanks to Snyk:
Join Securing Vibe Coding: Addressing the Security Challenges of AI-Generated Code on August 28 at 11 am ET with Snyk.
In this live session, host Sonya Moisset will cover:
• The security implications of Vibe Coding
• Actionable strategies to secure AI-generated code at scale, and
• How Snyk secures your AI-powered SDLC from code to deployment
Plus, ISC2 members will earn 1 CPE credit for attending live. Join Here!
Hottest News
1. Google DeepMind Is Rolling Out Gemini 2.5 Deep Think
Google is introducing Deep Think in the Gemini app for Google AI Ultra subscribers. This feature allows more “thinking time” through parallel reasoning techniques to better handle complex tasks, such as creative problem-solving, strategic planning, and step-by-step improvement. Deep Think is based on a variation of the model that recently reached gold-medal performance at the 2025 IMO. While that version takes hours to solve complex problems, Deep Think is designed for faster, everyday use and reaches bronze-level IMO performance in internal evaluations.
2. Chinese AI Lab Z.ai Launched GLM 4.5
Z.ai has released GLM‑4.5 and GLM‑4.5‑Air, two new Mixture‑of‑Experts models optimized for reasoning, coding, and agentic tasks. GLM‑4.5 ranks third overall on major benchmarks, showing strong performance in web browsing accuracy and multi-agent workflows. The flagship model features 355 billion total parameters (32 billion active), while the lighter GLM‑4.5‑Air uses 106 billion total and 12 billion active parameters, reducing hardware and compute footprint.
3. Mistral Released Codestral 25.08
Mistral has launched Codestral 25.08, delivering a 30% increase in accepted code suggestions, 10% more retained suggestions, 50% fewer runaway generations, and a 5% improvement in instruction-following. The release is part of Mistral’s full coding suite, which includes Devstral, Codestral Embed, and a Code IDE extension, now all publicly available as part of its complete AI coding stack.
4. Report From Menlo Ventures: Anthropic Surpasses OpenAI in Enterprise Usage
A report from Menlo Ventures shows Anthropic now holds 32% of the enterprise LLM market by usage, with OpenAI at 25%. Anthropic’s lead is even more pronounced in enterprise coding workloads, where it commands 42% of usage, double that of OpenAI. The report, based on a survey of 150+ enterprise leaders, also notes that enterprise spending on LLMs has more than doubled in the first half of 2025, rising from $3.5B to $8.4B. Most companies are prioritizing inference over model training, with code generation emerging as the first major breakout use case.
5. OpenAI Launches Study Mode in ChatGPT
OpenAI has introduced Study Mode in ChatGPT to support interactive, step-by-step learning. Designed with educator input, the mode uses Socratic questioning, scaffolded responses, and tailored guidance to promote critical thinking and long-term retention. OpenAI plans to evolve the feature based on educator feedback and ongoing research collaborations.
6. Anthropic Unveils New Rate Limits To Curb Claude Code Power Users
Anthropic is implementing weekly rate limits for its Claude AI coding tool to address misuse and overuse. The company cites cases of subscribers running Claude Code continuously or reselling access in violation of policy. Starting August 28, new limits will apply to Pro ($20/month), Max ($100/month), and Max Pro ($200/month) plans to maintain fair usage and system reliability.
Five 5-minute reads/videos to keep you learning
1. Explainable AI in Action: Health Risk Prediction with LangGraph, MCP, and SHAP
This project walks through building a transparent health risk prediction system using LangGraph, MCP, and SHAP. A scikit-learn model and SHAP explainer are converted into callable tools with the Model Context Protocol (MCP), then orchestrated by a LangGraph agent powered by a local Ollama LLM. The final product is a Streamlit chatbot that visualizes both predictions and their reasoning, offering an auditable and modular pipeline suited for sensitive use cases.
2. Everything You Need To Know About Context Engineering
This article introduces context engineering, the practice of structuring input to optimize LLM performance. It covers common pitfalls like “context rot” and the “lost in the middle” problem, and outlines strategies such as input organization, hierarchical memory, and coordination techniques for multi-agent systems.
3. Build Your Own Mini NotebookLM: Craft AI Podcasts with Python & Your Personal AI Brain
This article outlines a procedure for building a personal AI podcast generator on a local machine, creating a “Mini NotebookLM.” It explains how to use a local LLM, such as Gemma with Ollama, to generate a multi-speaker script. The guide provides Python code to manage the LLM interaction, parse the generated script, and use a Text-to-Speech model to create distinct voice clips.
4. How to Choose the Best LLM for Writing
This piece explores how to evaluate LLMs for writing tasks, looking beyond benchmark scores to consider creativity, emotional nuance, and narrative coherence. It covers techniques such as human evaluation, AI judges, static metrics, and tools like EQ‑Bench to assess emotional intelligence in writing models.
5. A Comprehensive Guide on Prompt Injection-Part 1
Part one of this guide tackles prompt injection vulnerabilities, explaining direct, indirect, and obfuscated attacks. It proposes layered defenses, including prompt hardening, input/output sanitization, privilege isolation, and system/user prompt separation, along with the importance of robust monitoring and human-in-the-loop controls.
Repositories & Tools
1. Trackio is a lightweight, free experiment tracking Python library built on top of HuggingFace Datasets and Spaces.
2. OpenCode is an AI coding agent built for the terminal.
3. AgentSociety is an advanced framework designed for building agents in urban simulation environments.
4. Ladybird is an independent web browser, using a novel engine based on web standards.
Top Papers of The Week
1. A Survey of Self-Evolving Agents: On Path to Artificial Super Intelligence
This survey organizes efforts around evolving agent components and adaptation methods, analyzing algorithmic designs, evaluation metrics, and applications in coding, education, and healthcare. It highlights challenges in safety and scalability, aiming to design agents that autonomously perform beyond human intelligence.
2. Agentic Reinforced Policy Optimization
This paper proposes Agentic Reinforced Policy Optimization (ARPO), a new reinforcement learning algorithm that enhances LLMs for multi-turn reasoning tasks involving external tools. By employing an entropy-based adaptive rollout mechanism and advantage attribution estimation, ARPO outperforms existing methods, halving the tool-use budget required and aligning LLM-based agents with dynamic environments.
3. MLE-STAR: Machine Learning Engineering Agent via Search and Targeted Refinement
This paper introduces MLE-STAR (Machine Learning Engineering via Search and Targeted Refinement), a state-of-the-art agent system to automate complex ML pipeline design and optimization. MLE-STAR first leverages external knowledge by using a search engine to retrieve effective models from the web, forming an initial solution, then iteratively refines it by exploring various strategies targeting specific ML components.
4. Seed-Prover: Deep and Broad Reasoning for Automated Theorem Proving
This paper proposes Seed-Prover, a lemma-style whole-proof reasoning model that significantly advances automated theorem proving. It refines proofs using Lean feedback and self-summarization, achieving 78.1% success on formalized IMO problems. Seed-Geometry enhances geometry reasoning, collectively proving 5 out of 6 IMO 2025 problems, showcasing the power of formal verification and deep reasoning.
This paper introduces a modular multi-agent framework that performs UI-to-code generation in three stages: grounding, planning, and generation. The grounding agent uses a vision-language model to detect and label UI components, the planning agent constructs a hierarchical layout using front-end engineering priors, and the generation agent produces HTML/CSS code via adaptive prompt-based synthesis.
Quick Links
1. Quora’s AI platform Poe is releasing an API that lets developers integrate various models or bots into their own applications. The API doesn’t require a separate fee; usage is tracked through Poe’s existing point-based subscription system, with each model call deducting a set number of points.
2. Anthropic cuts off OpenAI’s access to its Claude models. According to Wired, OpenAI was using Claude through internal tools to benchmark its own models on tasks like coding, writing, and safety, prompting Anthropic to revoke access.
3. Google is adding new capabilities to AI Mode, including Canvas, a tool that helps users build study plans and organize content across sessions in a persistent side panel. U.S. users enrolled in the AI Mode Labs experiment will begin seeing Canvas in the coming weeks.
Who’s Hiring in AI
Senior Software Engineer, AI Enablement @Reddit (Remote/USA)
Senior Software Engineer (AI) @Bentley Systems (Ireland, UK, Netherlands, or Portugal)
Software Engineer AI Development @WindStream Communications (Remote)
AI Engineer (Associate) @Huron Consulting Group (Remote)
Software Developer @ASRC Federal Holding Company (Remote/USA)
Sr Intelligent Automation Developer @Oshkosh Corporation (Multiple US Locations)
Group Manager, Software Engineering @Concentrix (GA, USA/WFH)
Interested in sharing a job opportunity here? Contact sponsors@towardsai.net.
Think a friend would enjoy this too? Share the newsletter and let them join the conversation.






Your target is to control a cube reach the end of the road in https://geometrydashs.io